📌 MAROKO133 Eksklusif ai: Adobe Research Unlocking Long-Term Memory in Video World
Video world models, which predict future frames conditioned on actions, hold immense promise for artificial intelligence, enabling agents to plan and reason in dynamic environments. Recent advancements, particularly with video diffusion models, have shown impressive capabilities in generating realistic future sequences. However, a significant bottleneck remains: maintaining long-term memory. Current models struggle to remember events and states from far in the past due to the high computational cost associated with processing extended sequences using traditional attention layers. This limits their ability to perform complex tasks requiring sustained understanding of a scene.
A new paper, “Long-Context State-Space Video World Models” by researchers from Stanford University, Princeton University, and Adobe Research, proposes an innovative solution to this challenge. They introduce a novel architecture that leverages State-Space Models (SSMs) to extend temporal memory without sacrificing computational efficiency.
The core problem lies in the quadratic computational complexity of attention mechanisms with respect to sequence length. As the video context grows, the resources required for attention layers explode, making long-term memory impractical for real-world applications. This means that after a certain number of frames, the model effectively “forgets” earlier events, hindering its performance on tasks that demand long-range coherence or reasoning over extended periods.
The authors’ key insight is to leverage the inherent strengths of State-Space Models (SSMs) for causal sequence modeling. Unlike previous attempts that retrofitted SSMs for non-causal vision tasks, this work fully exploits their advantages in processing sequences efficiently.
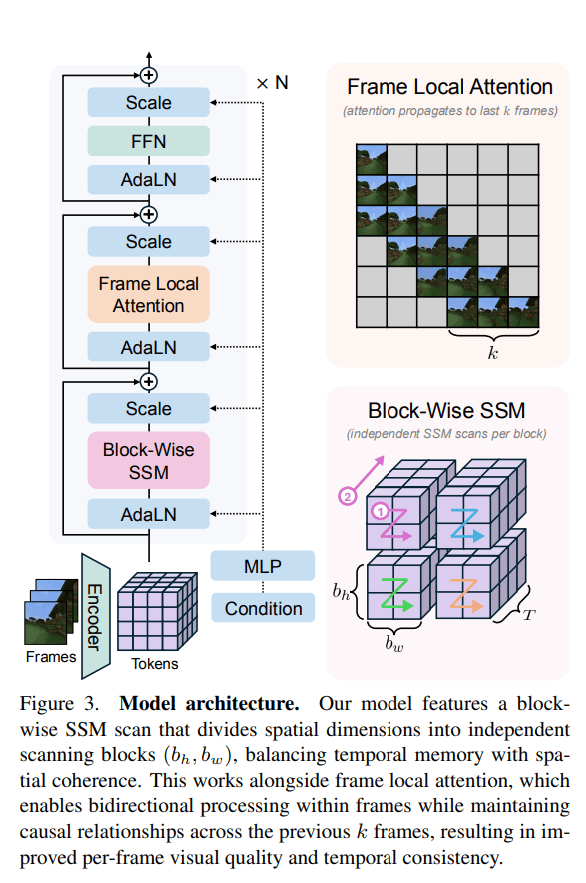
The proposed Long-Context State-Space Video World Model (LSSVWM) incorporates several crucial design choices:
- Block-wise SSM Scanning Scheme: This is central to their design. Instead of processing the entire video sequence with a single SSM scan, they employ a block-wise scheme. This strategically trades off some spatial consistency (within a block) for significantly extended temporal memory. By breaking down the long sequence into manageable blocks, they can maintain a compressed “state” that carries information across blocks, effectively extending the model’s memory horizon.
- Dense Local Attention: To compensate for the potential loss of spatial coherence introduced by the block-wise SSM scanning, the model incorporates dense local attention. This ensures that consecutive frames within and across blocks maintain strong relationships, preserving the fine-grained details and consistency necessary for realistic video generation. This dual approach of global (SSM) and local (attention) processing allows them to achieve both long-term memory and local fidelity.
The paper also introduces two key training strategies to further improve long-context performance:
- Diffusion Forcing: This technique encourages the model to generate frames conditioned on a prefix of the input, effectively forcing it to learn to maintain consistency over longer durations. By sometimes not sampling a prefix and keeping all tokens noised, the training becomes equivalent to diffusion forcing, which is highlighted as a special case of long-context training where the prefix length is zero. This pushes the model to generate coherent sequences even from minimal initial context.
- Frame Local Attention: For faster training and sampling, the authors implemented a “frame local attention” mechanism. This utilizes FlexAttention to achieve significant speedups compared to a fully causal mask. By grouping frames into chunks (e.g., chunks of 5 with a frame window size of 10), frames within a chunk maintain bidirectionality while also attending to frames in the previous chunk. This allows for an effective receptive field while optimizing computational load.
The researchers evaluated their LSSVWM on challenging datasets, including Memory Maze and Minecraft, which are specifically designed to test long-term memory capabilities through spatial retrieval and reasoning tasks.
The experiments demonstrate that their approach substantially surpasses baselines in preserving long-range memory. Qualitative results, as shown in supplementary figures (e.g., S1, S2, S3), illustrate that LSSVWM can generate more coherent and accurate sequences over extended periods compared to models relying solely on causal attention or even Mamba2 without frame local attention. For instance, on reasoning tasks for the maze dataset, their model maintains better consistency and accuracy over long horizons. Similarly, for retrieval tasks, LSSVWM shows improved ability to recall and utilize information from distant past frames. Crucially, these improvements are achieved while maintaining practical inference speeds, making the models suitable for interactive applications.
The Paper Long-Context State-Space Video World Models is on arXiv
The post Adobe Research Unlocking Long-Term Memory in Video World Models with State-Space Models first appeared on Synced.
🔗 Sumber: syncedreview.com
📌 MAROKO133 Update ai: Hyundai’s award-winning droid conquers slopes and uneven su
Hyundai has long been a name synonymous with the roar of engines and the sleek lines of sedans. But at the Consumer Electronics Show 2026 in Las Vegas, the South Korean giant, Hyundai Motor Company, made history.
For the first time, Hyundai Motor Group’s Robotics LAB has secured the prestigious Best of Innovation Award in Robotics at CES 2026 for its MobED (Mobile Eccentric Droid).
The tiny four-wheeled droid has been designed to navigate complex environments that typically challenge robots.
Interestingly, the wheels allow the robot to climb steep ramps or roll over high curbs.
With both Basic and Pro models, MobED meets specific needs across various industries and lifestyle applications.
“This recognition highlights the Group’s advancements in robotics technology and its commitment to redefining mobility solutions,” a press statement released on January 5 noted.
MobED can tackle “last-mile” logistics by simplifying complex deliveries and serves as a tool for the service industry, where it can act as a digital guide, broadcasting assistant, or mobile advertising platform.
Drive and Lift technology
The product was first unveiled at the International Robot Exhibition 2025 (iREX 2025) in Tokyo, Japan, in December 2025.
MobED is based on Hyundai’s proprietary Drive and Lift (DnL) technology, a sophisticated system that allows the robot to master difficult terrain.
With each wheel independently adjustable, the platform maintains a perfectly level surface even on steep inclines, high curbs, or rocky ground. This ensures that whether the robot is carrying a fragile delivery or a high-end camera, it remains stable and secure in any environment.
It comes in two models — MobED Basic and MobED Pro.
The pro model robot is the brainy sibling. Packed with a fusion of LiDAR and camera sensors, it uses AI-based algorithms to navigate crowded city sidewalks autonomously. Moreover, it even features a “follow-me” mode that acts as a tireless companion for commercial users.
On the other hand, the basic model is a controller-operated platform designed for researchers and developers to build their own custom applications upon.
Earlier, Hyundai stated that it is set to bring MobED to the commercial market in the first half of 2026, offering both the Basic and Pro models for industrial and consumer purchase.
Payload capacity
MobED features a minimalist, balanced design that prioritizes functionality. The platform can safely transition between tight indoor hallways and rough outdoor environments.
Its modular setup allows for various top-mounted attachments — like delivery boxes, equipment, or screens — making it ideal for logistics, broadcasting, and guidance services.
The platform is a powerhouse, supporting up to 47 kg (103 pounds) on the Basic model and 57 kg (125 pounds) on the Pro model. Moreover, the pro model reaches top speeds of 10 km/h (approximately 2.8m/s).
This award marks a key moment in Hyundai’s evolution into a “Smart Mobility Solution Provider.”
Visitors at the Hyundai exhibit this week are already seeing MobED in action, navigating simulated urban obstacle courses with eerie precision.
You won’t have to wait long to see one in the wild, either. Mass production is officially slated to begin in early 2026.
🔗 Sumber: interestingengineering.com
🤖 Catatan MAROKO133
Artikel ini adalah rangkuman otomatis dari beberapa sumber terpercaya. Kami pilih topik yang sedang tren agar kamu selalu update tanpa ketinggalan.
✅ Update berikutnya dalam 30 menit — tema random menanti!