📌 MAROKO133 Update ai: Adobe Research Unlocking Long-Term Memory in Video World Mo
Video world models, which predict future frames conditioned on actions, hold immense promise for artificial intelligence, enabling agents to plan and reason in dynamic environments. Recent advancements, particularly with video diffusion models, have shown impressive capabilities in generating realistic future sequences. However, a significant bottleneck remains: maintaining long-term memory. Current models struggle to remember events and states from far in the past due to the high computational cost associated with processing extended sequences using traditional attention layers. This limits their ability to perform complex tasks requiring sustained understanding of a scene.
A new paper, “Long-Context State-Space Video World Models” by researchers from Stanford University, Princeton University, and Adobe Research, proposes an innovative solution to this challenge. They introduce a novel architecture that leverages State-Space Models (SSMs) to extend temporal memory without sacrificing computational efficiency.
The core problem lies in the quadratic computational complexity of attention mechanisms with respect to sequence length. As the video context grows, the resources required for attention layers explode, making long-term memory impractical for real-world applications. This means that after a certain number of frames, the model effectively “forgets” earlier events, hindering its performance on tasks that demand long-range coherence or reasoning over extended periods.
The authors’ key insight is to leverage the inherent strengths of State-Space Models (SSMs) for causal sequence modeling. Unlike previous attempts that retrofitted SSMs for non-causal vision tasks, this work fully exploits their advantages in processing sequences efficiently.
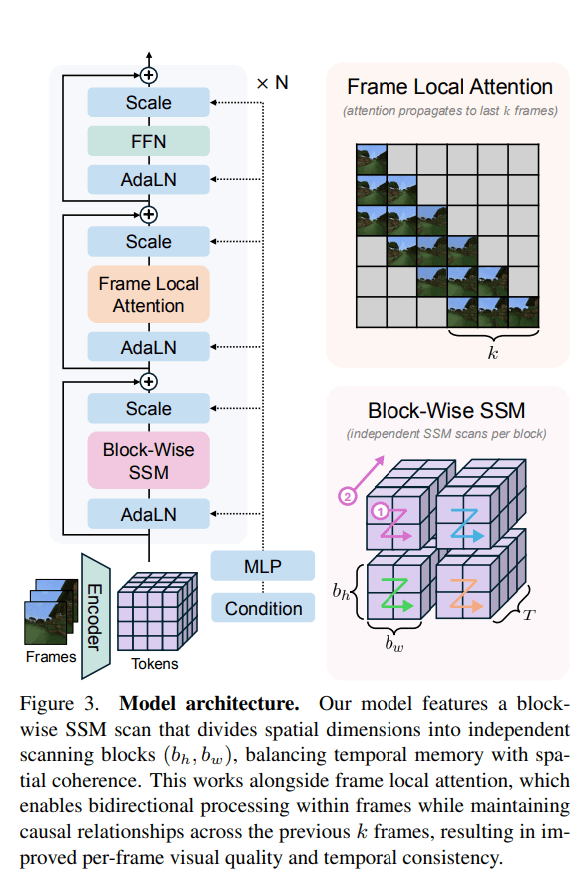
The proposed Long-Context State-Space Video World Model (LSSVWM) incorporates several crucial design choices:
- Block-wise SSM Scanning Scheme: This is central to their design. Instead of processing the entire video sequence with a single SSM scan, they employ a block-wise scheme. This strategically trades off some spatial consistency (within a block) for significantly extended temporal memory. By breaking down the long sequence into manageable blocks, they can maintain a compressed “state” that carries information across blocks, effectively extending the model’s memory horizon.
- Dense Local Attention: To compensate for the potential loss of spatial coherence introduced by the block-wise SSM scanning, the model incorporates dense local attention. This ensures that consecutive frames within and across blocks maintain strong relationships, preserving the fine-grained details and consistency necessary for realistic video generation. This dual approach of global (SSM) and local (attention) processing allows them to achieve both long-term memory and local fidelity.
The paper also introduces two key training strategies to further improve long-context performance:
- Diffusion Forcing: This technique encourages the model to generate frames conditioned on a prefix of the input, effectively forcing it to learn to maintain consistency over longer durations. By sometimes not sampling a prefix and keeping all tokens noised, the training becomes equivalent to diffusion forcing, which is highlighted as a special case of long-context training where the prefix length is zero. This pushes the model to generate coherent sequences even from minimal initial context.
- Frame Local Attention: For faster training and sampling, the authors implemented a “frame local attention” mechanism. This utilizes FlexAttention to achieve significant speedups compared to a fully causal mask. By grouping frames into chunks (e.g., chunks of 5 with a frame window size of 10), frames within a chunk maintain bidirectionality while also attending to frames in the previous chunk. This allows for an effective receptive field while optimizing computational load.
The researchers evaluated their LSSVWM on challenging datasets, including Memory Maze and Minecraft, which are specifically designed to test long-term memory capabilities through spatial retrieval and reasoning tasks.
The experiments demonstrate that their approach substantially surpasses baselines in preserving long-range memory. Qualitative results, as shown in supplementary figures (e.g., S1, S2, S3), illustrate that LSSVWM can generate more coherent and accurate sequences over extended periods compared to models relying solely on causal attention or even Mamba2 without frame local attention. For instance, on reasoning tasks for the maze dataset, their model maintains better consistency and accuracy over long horizons. Similarly, for retrieval tasks, LSSVWM shows improved ability to recall and utilize information from distant past frames. Crucially, these improvements are achieved while maintaining practical inference speeds, making the models suitable for interactive applications.
The Paper Long-Context State-Space Video World Models is on arXiv
The post Adobe Research Unlocking Long-Term Memory in Video World Models with State-Space Models first appeared on Synced.
🔗 Sumber: syncedreview.com
📌 MAROKO133 Update ai: Claude Code costs up to $200 a month. Goose does the same t
The artificial intelligence coding revolution comes with a catch: it's expensive.
Claude Code, Anthropic's terminal-based AI agent that can write, debug, and deploy code autonomously, has captured the imagination of software developers worldwide. But its pricing — ranging from $20 to $200 per month depending on usage — has sparked a growing rebellion among the very programmers it aims to serve.
Now, a free alternative is gaining traction. Goose, an open-source AI agent developed by Block (the financial technology company formerly known as Square), offers nearly identical functionality to Claude Code but runs entirely on a user's local machine. No subscription fees. No cloud dependency. No rate limits that reset every five hours.
"Your data stays with you, period," said Parth Sareen, a software engineer who demonstrated the tool during a recent livestream. The comment captures the core appeal: Goose gives developers complete control over their AI-powered workflow, including the ability to work offline — even on an airplane.
The project has exploded in popularity. Goose now boasts more than 26,100 stars on GitHub, the code-sharing platform, with 362 contributors and 102 releases since its launch. The latest version, 1.20.1, shipped on January 19, 2026, reflecting a development pace that rivals commercial products.
For developers frustrated by Claude Code's pricing structure and usage caps, Goose represents something increasingly rare in the AI industry: a genuinely free, no-strings-attached option for serious work.
Anthropic's new rate limits spark a developer revolt
To understand why Goose matters, you need to understand the Claude Code pricing controversy.
Anthropic, the San Francisco artificial intelligence company founded by former OpenAI executives, offers Claude Code as part of its subscription tiers. The free plan provides no access whatsoever. The Pro plan, at $17 per month with annual billing (or $20 monthly), limits users to just 10 to 40 prompts every five hours — a constraint that serious developers exhaust within minutes of intensive work.
The Max plans, at $100 and $200 per month, offer more headroom: 50 to 200 prompts and 200 to 800 prompts respectively, plus access to Anthropic's most powerful model, Claude 4.5 Opus. But even these premium tiers come with restrictions that have inflamed the developer community.
In late July, Anthropic announced new weekly rate limits. Under the system, Pro users receive 40 to 80 hours of Sonnet 4 usage per week. Max users at the $200 tier get 240 to 480 hours of Sonnet 4, plus 24 to 40 hours of Opus 4. Nearly five months later, the frustration has not subsided.
The problem? Those "hours" are not actual hours. They represent token-based limits that vary wildly depending on codebase size, conversation length, and the complexity of the code being processed. Independent analysis suggests the actual per-session limits translate to roughly 44,000 tokens for Pro users and 220,000 tokens for the $200 Max plan.
"It's confusing and vague," one developer wrote in a widely shared analysis. "When they say '24-40 hours of Opus 4,' that doesn't really tell you anything useful about what you're actually getting."
The backlash on Reddit and developer forums has been fierce. Some users report hitting their daily limits within 30 minutes of intensive coding. Others have canceled their subscriptions entirely, calling the new restrictions "a joke" and "unusable for real work."
Anthropic has defended the changes, stating that the limits affect fewer than five percent of users and target people running Claude Code "continuously in the background, 24/7." But the company has not clarified whether that figure refers to five percent of Max subscribers or five percent of all users — a distinction that matters enormously.
How Block built a free AI coding agent that works offline
Goose takes a radically different approach to the same problem.
Built by Block, the payments company led by Jack Dorsey, Goose is what engineers call an "on-machine AI agent." Unlike Claude Code, which sends your queries to Anthropic's servers for processing, Goose can run entirely on your local computer using open-source language models that you download and control yourself.
The project's documentation describes it as going "beyond code suggestions" to "install, execute, edit, and test with any LLM." That last phrase — "any LLM" — is the key differentiator. Goose is model-agnostic by design.
You can connect Goose to Anthropic's Claude models if you have API access. You can use OpenAI's GPT-5 or Google's Gemini. You can route it through services like Groq or OpenRouter. Or — and this is where things get interesting — you can run it entirely locally using tools like Ollama, which let you download and execute open-source models on your own hardware.
The practical implications are significant. With a local setup, there are no subscription fees, no usage caps, no rate limits, and no concerns about your code being sent to external servers. Your conversations with the AI never leave your machine.
"I use Ollama all the time on planes — it's a lot of fun!" Sareen noted during a demonstration, highlighting how local models free developers from the constraints of internet connectivity.
What Goose can do that traditional code assistants can't
Goose operates as a command-line tool or desktop application that can autonomously perform complex development tasks. It can build entire projects from scratch, write and execute code, debug failures, orchestrate workflows across multiple files, and interact with external APIs — all without constant human oversight.
The architecture relies on what the AI industry calls "tool calling" or "<a href="https://platform.openai…
Konten dipersingkat otomatis.
🔗 Sumber: venturebeat.com
🤖 Catatan MAROKO133
Artikel ini adalah rangkuman otomatis dari beberapa sumber terpercaya. Kami pilih topik yang sedang tren agar kamu selalu update tanpa ketinggalan.
✅ Update berikutnya dalam 30 menit — tema random menanti!